About disease
Species
- Type I: Insulin-dependent or childhood diabetes. Usually occurs during childhood or adolescence. Caused by damage to pancreatic cells due to lack of insulin in the body. People with this type of diabetes require constant use of external insulin.
- Type II: Non-insulin-dependent or adult-onset diabetes. It occurs most commonly in adulthood, but is now also common in children and teenagers. It is caused by the body's tissues being insensitive to insulin, so they cannot absorb glucose properly. People with this type of diabetes can control blood sugar levels through proper diet, physical activity, and blood sugar-lowering medications. In severe cases, insulin may be needed.
- Mild (HbA1c less than 6. 5%): blood sugar level is within the normal range or close to normal, and there are few pathological manifestations.
- Moderate (HbA1c 6. 5-7. 9%): Slightly elevated blood sugar levels with specific symptoms or early signs of complications.
- Severe (HbA1c 8% or higher): Characterized by significant blood sugar levels and severe symptoms and complications.
symptoms of diabetes
- Frequent urinary urgency and increased urine output;
- Intense thirst and consumption of large amounts of fluid;
- Dry oral mucosa;
- decreased vision and dizziness;
- Obvious appetite and overeating;
- Ulcers appear on different parts of the skin, and wound healing takes longer;
- Insomnia, fatigue;
- performance degradation;
- Unexplained weight loss or obesity;
- Infectious diseases occur frequently.
causes of diabetes
- Genetic disorders that lead to the development of autoimmune diseases and pancreatic pathology. Having a relative with diabetes is an important risk factor;
- obesity. The accumulation of excess adipose tissue can lead to metabolic disorders and make the tissue less sensitive to insulin;
- Immune dysfunction, characterized by damage to pancreatic tissue;
- Effects of viral infections and toxins on the pancreas;
- taking corticosteroids and other medications that contribute to the development of diabetes;
- Adrenal gland dysfunction;
- Cardiovascular pathology.
Diagnosis of diabetes
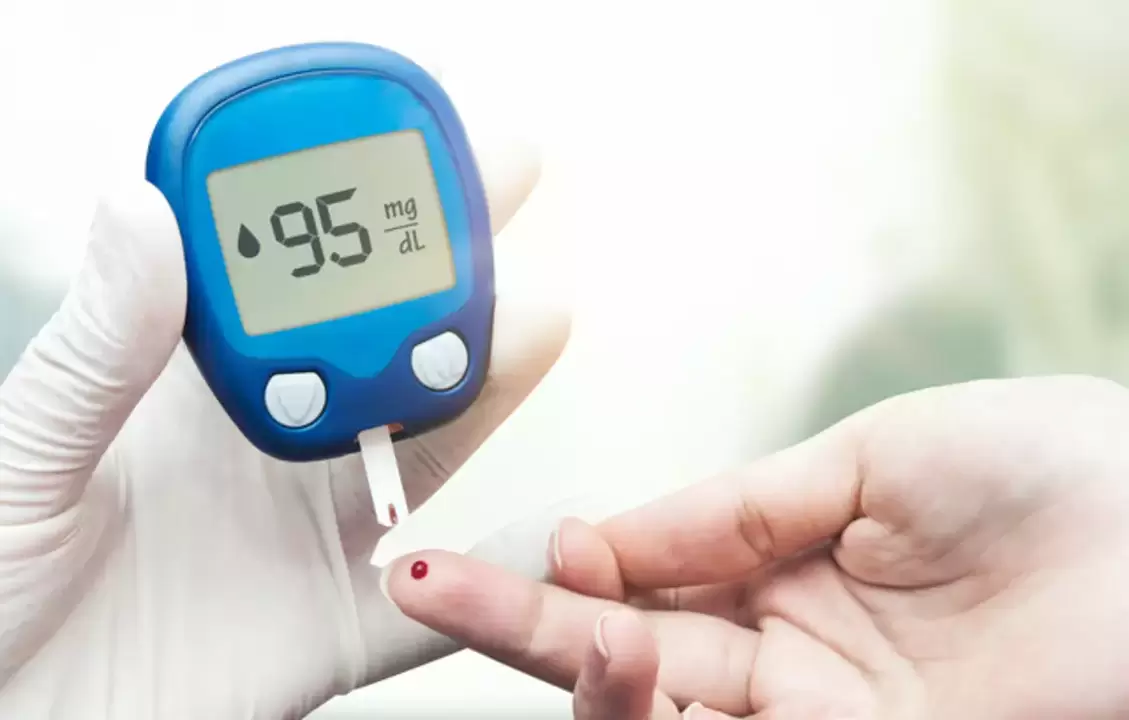
- Fasting blood test. Endocrinologists ask patients not to eat in the hours before bed and in the morning before the study. During the procedure, the specialist treats the skin of the fingers with antiseptic, makes a small puncture using a scarifier, and collects a small amount of blood in a special container. A sign of diabetes may be that the glucose content in the sample obtained exceeds 6. 5mmol/l;
- Blood tests for glycated hemoglobin levels. Levels of this substance can indicate glucose levels in the blood over a 3-month period, so doctors prescribe such tests for initial diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes treatment. A glycosylated hemoglobin concentration higher than 6. 5% indicates the presence of diabetes;
- Load testing. The first phase of the study was a standard measurement of fasting blood glucose levels. The doctor then asked the patient to drink a glass of water with sugar, and 2 hours later performed another blood test. The diagnosis is confirmed if the first test results show moderate blood glucose levels (up to 6. 5 mmol/L) and the second test shows significantly elevated blood glucose levels (about 11 mmol/L);
- Blood tests for C-peptide levels. Endocrinologists prescribe this test to reliably assess insulin production over time;
- Get a blood test anytime. This test is used to confirm signs of disease. Glucose concentrations exceeding 10 mmol/L in some blood samples, regardless of meal time, indicate the presence of diabetes;
- Urinalysis. People with diabetes have high levels of glucose in their urine. In addition, patients may have ketone bodies in their urine, indicating a disorder in glucose metabolism.
Expert opinion
diabetes treatment
- Medications to lower blood sugar levels are prescribed. Depending on the diagnosis and the patient's medical history, the endocrinologist may prescribe a sulfonylurea, meglitinide, alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, biguanide, or thiazolidinedione. It is often necessary to take multiple medications, strictly adhere to dosages, and monitor blood sugar levels. Listed drugs improve insulin production by the pancreas, stimulate tissue sensitivity to glucose, and reduce glucose uptake from food;
- Insulin is administered by injection. Endocrinologists prescribe such treatments for all patients with type 1 diabetes and for patients with type 2 diabetes if medications to lower blood sugar levels are ineffective or contraindicated. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes can also receive insulin treatment. First, the endocrinologist prescribes a long-acting insulin injection—a drug that must be taken once a day, regardless of nutrition. Rapid-acting insulin preparations are used in hospitals to treat complex diabetes and conditions in which blood sugar levels rise sharply. The doctor explains the rules of the injection and the required dosage. The consultation also explains the importance of regular monitoring of blood sugar levels using a glucometer.
Prevent diabetes
- weight normalization and moderate physical activity;
- Prompt treatment of pancreatic diseases;
- Eat a healthy diet, including plenty of vegetables and fruits.